Home > News & Blog > Most Comprehensive Introduction to Glass Tempering Furnaces
Glass tempering is a vital process in the glass industry, providing a range of benefits that enhance the performance and safety of glass products. From its strength to its versatility, tempered glass offers significant advantages for various applications. In this blog, we'll explore the benefits of glass tempering and how specialized glass tempering furnaces make this possible. We'll also cover the equipment, technology, and standards involved in the tempering process, as well as the key applications of tempered glass in different industries.
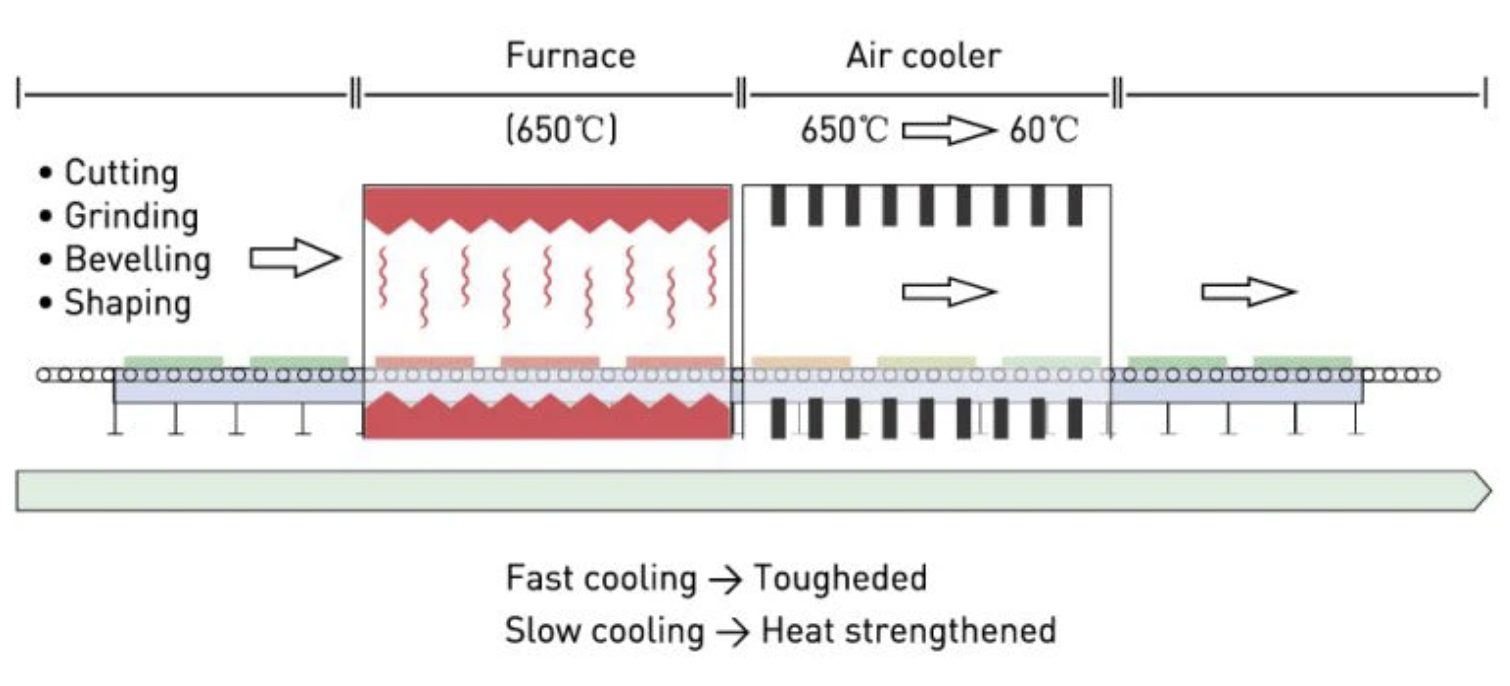
Tempered glass, often referred to as toughened glass, is significantly stronger than regular glass. It undergoes a thermal treatment process inside a glass tempering furnace, where the glass is heated to high temperatures and then rapidly cooled by a cooling blower. This results in the formation of compressive stress on the surface, making it four to five times stronger than untreated glass.
One of the main benefits of tempered glass is its safety. Unlike regular glass, which shatters into large, sharp pieces, tempered glass breaks into small, blunt fragments, reducing the risk of injury. This makes it suitable for applications like insulating glass in buildings and vehicles. Heat-strengthened glass also goes through a similar process, but while it offers some increased strength, it doesn’t match the robustness of fully tempered glass.
Tempered glass can also be laminated, creating laminated safety glass, which enhances security by keeping the glass intact even when shattered. This makes tempered glass a top choice in areas where human safety is a concern, such as architectural and automotive applications.
The unique properties of tempered glass make it highly suitable for various industries, helping to meet the specific challenges they face:
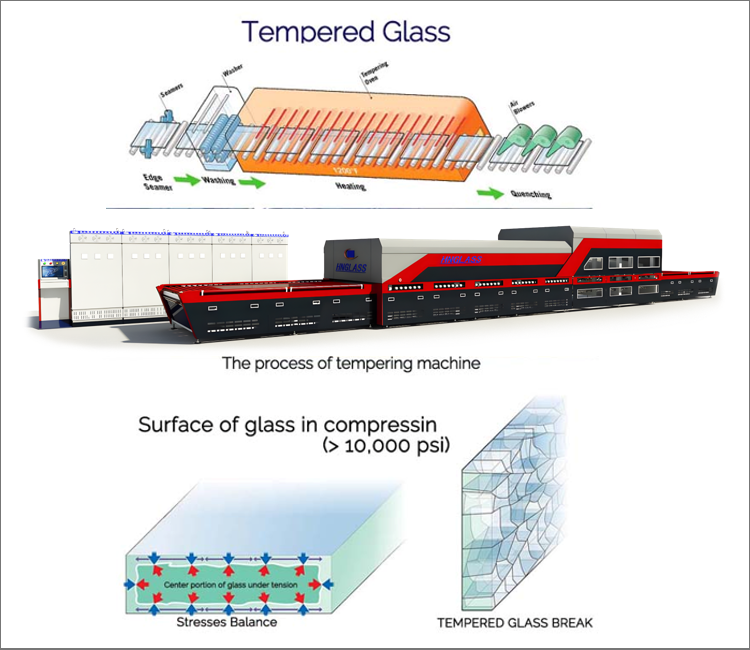
The process of glass tempering requires precise equipment, and glass tempering machines play a critical role in ensuring quality. A modern flat glass tempering furnace is designed with an efficient control system to manage heating, cooling, and quenching phases. These machines come equipped with technologies to process various types of glass, including soft-coated glass, which is more sensitive to heat.
Another key component of the tempering process is the cooling blower, which rapidly cools the glass during the quenching phase. This cooling must be uniform across the glass surface to achieve the desired strength and stress profile. Glass processing using these machines ensures consistency in thickness and stress distribution, improving overall product quality.

The glass tempering process is technologically advanced, involving precise heating and cooling mechanisms. First, the glass is heated in the tempering furnace to a temperature of around 620°C to 680°C. Once it reaches the ideal temperature, the glass is cooled rapidly by a high-pressure cooling blower. The result is the creation of surface compressive stress and inner tensile stress, which provides the glass with its enhanced strength.
In recent years, developments in glass production technology have made it possible to temper a wider range of glass types. For example, soft-coated glass, used in energy-efficient windows, can now be tempered thanks to advancements in tempering machines that offer precise temperature controls and shorter cycle times. This allows manufacturers to meet growing demand for insulating glass in sustainable construction projects.
There are various types of tempering furnaces designed for different industrial applications. These include heat treat ovens and industrial heat treat furnaces, which are used for producing a variety of tempered glass products, from architectural to automotive glass.
Flat glass, in particular, is processed using a flat glass tempering furnace, which can handle large glass sheets with uniform thickness. Other specialized furnaces are used for specific glass applications, such as heat treat ovens designed for curved or bent glass.
Tempered glass must comply with strict glass tempering standards and regulations to ensure safety and durability. In many countries, tempered glass is classified as safety glass and is required for certain architectural uses, such as windows, doors, and railings.
Regulatory bodies set specific guidelines on the thickness, strength, and safety performance of tempered glass, and manufacturers must adhere to these standards. This ensures that tempered glass products meet the required safety and quality specifications for various uses, from insulating glass to automotive windshields.
The glass tempering process offers many benefits, from enhanced strength and safety to flexibility in application. Advanced glass tempering furnaces and equipment ensure that the process is efficient, precise, and compliant with industry regulations. Whether used in building projects, the automotive sector, or even solar energy applications, tempered glass continues to be a crucial material in modern engineering and design.
By utilizing state-of-the-art glass tempering machines with sophisticated control systems, manufacturers can produce high-quality tempered glass that meets the challenges of today's industries, providing safer, stronger, and more durable glass solutions.